From prevision to recovery: Forestland wildfires risk management in Spain
Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya
The Institut Cartogràfic i Geològic de Catalunya is a public organisation that provides rigorous and quality information about the territory to address the challenges of our society, such as climate change, risk and natural resource management, sustainable development or energy transition. Their duties are related to the competences of geodesy and cartography and about the spatial data infrastructure of Catalonia, and also the competences of promoting and carrying out the actions related to the awareness, survey and information about the soil and subsoil. Their expertise and knowledge facilitate decision making and places them among the leading institutes at an international level in the field of geoinformation. They guarantee the officiality and independence of the (geo)information and services ranging from data capture to the implementation of solutions.
They use space to Observe to Understand. Understand to act.
The challenge
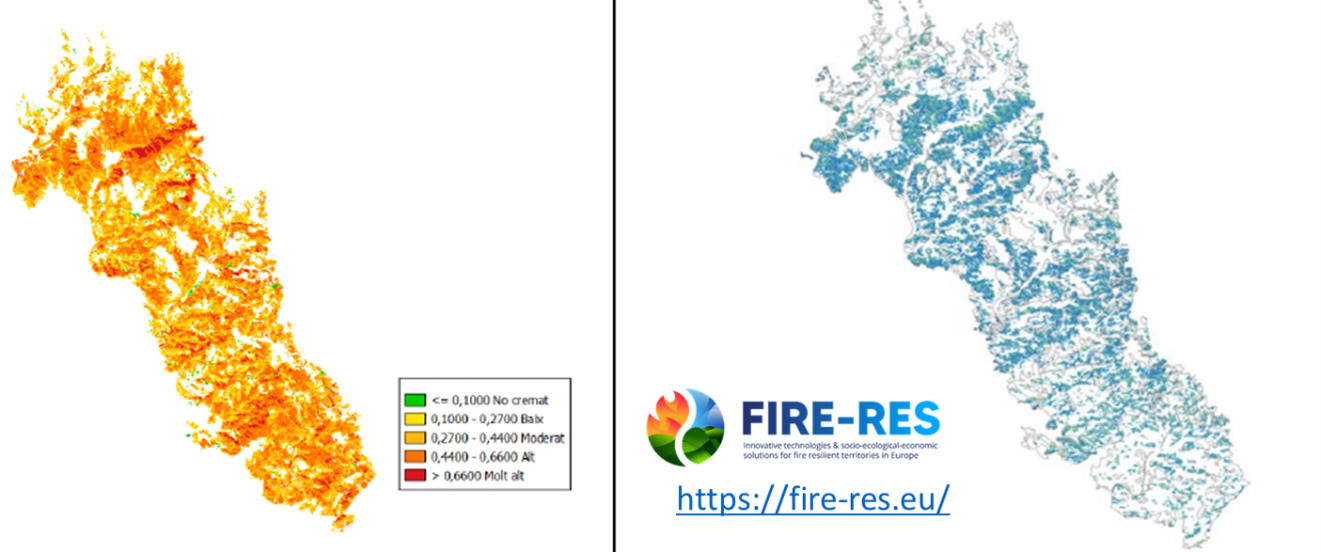
Spain has seen an increase in occurrence of wildfires in recent years. In addition, close to 65% of the Catalan territory is covered by forestland. Thus, the ability to avoid collapse in the face of extreme fires by identifying, developing and deploying innovative means that promote landscape resilience becomes crucial. To limit the damage of fires on forests and take better preventive measures to avoid them, ICGC carried out thanks to Earth observation assets, innovative developments to evaluate the state of forestland, key metrics on forest morphology, urban-forest interface status, recovery-resilience of forestland covers, to assure socio, economic and ecosystem values of the forestland.
The satellite solution
The ICGC uses several satellite missions to obtain key forestland metrics to improve preventive measures and analyse recovery from forestland wildfires, mainly Copernicus. Data from Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 satellites are used for vegetation monitoring, burnt area mapping and status of pathways and Wildland-Urban Interface key elements for firefighters. The Copernicus Emergency Management Service (CEMS) also provides rapid mapping for fires during the disaster and mapping of the resilience of forestland and its evolution. More information about Earth Observation activities at:
https://www.icgc.cat/en/Thematic-areas/Earth-Observation
The results
Using the fire risk information provided by the ICGC maps, Catalunya can make decisions to reallocate resources—such as helicopters, fire engines, and firefighting teams—from prevention to active response and forestland management. This enables timely action and helps identify the most effective routes to maximize impact and minimise losses.
